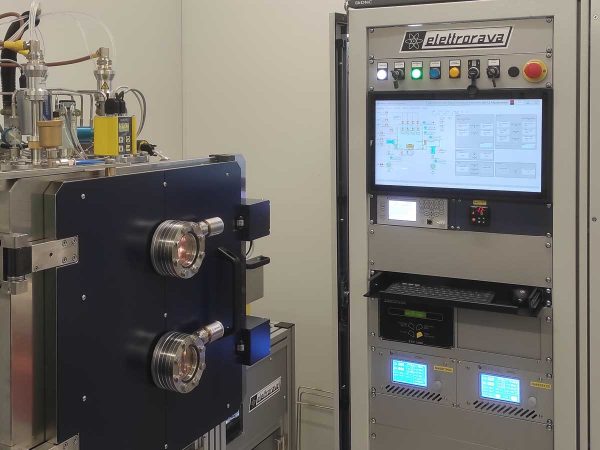
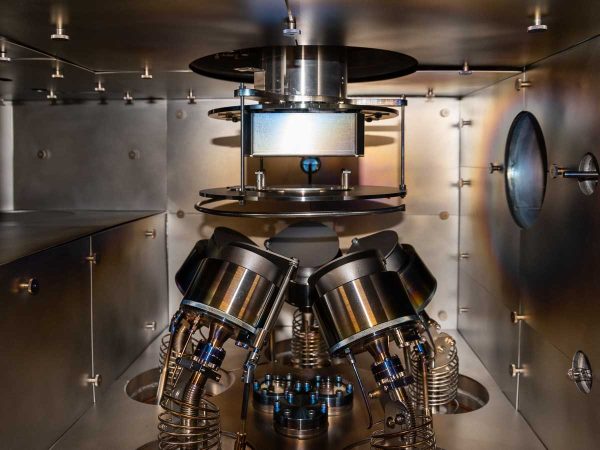
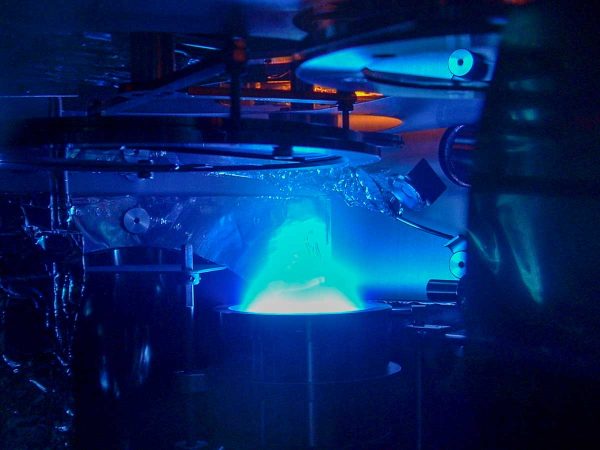
Sputtering process
Magnetron Sputtering
MS
Magnetron sputtering is a versatile deposition technique used to create thin films on a substrate surface by sputtering atoms or molecules from a target material. It offers a good deposition rate and the ability to deposit a wide range of materials including metals, dielectrics, and semiconductors. In this process, an Argon plasma is ignited above a negatively biased and magnetized target material, drawing ions from the plasma towards the target material. As a result, Argon ions impact the target, causing atoms or molecules to be ejected from the surface through a process known as sputtering. The sputtered material forms a vapour that condenses on the substrate surface, resulting in the formation of a thin film
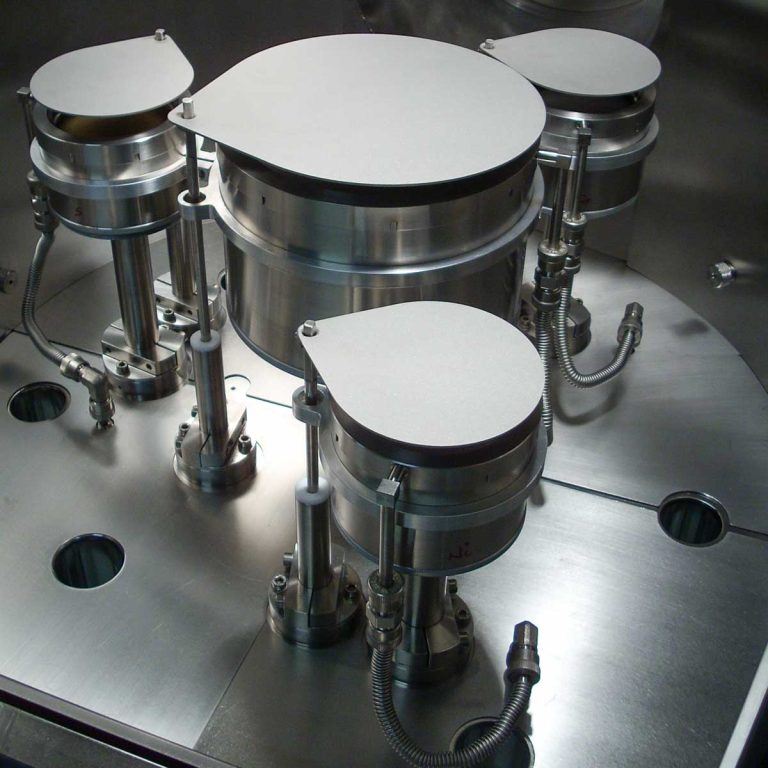

Applications
Magnetron sputtering can be used to deposit to create optical antireflective coatings, anticorrosive coatings, IR optics, dental protheses, and super-insulation. This deposition method is also employed in microelectronics for producing metal film capacitors, optical data storage, and microprocessors, as well as in the consumer industry for manufacturing anti-reflective coatings
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive Industry
- Solar Energy
- Aerospace and defence
- Healthcare and medical devices
- Optics and photonics
- Surface engineering
Key features
- Single, vertical coplanar, confocal or linear configuration sources can be combined for DC, DC pulsed, RF, HIPIMS
- Co-sputtering configuration
- Reactive gases (02 , N2 , etc) can be added for direct reaction during deposition process
- Integrated quartz crystal controller for thickness monitoring
- Optional automatic or manual load lock (optional pre-heating and/or plasma treatments)
- Optional wide range optical thickness monitor for the control of layer thickness for a large number of layers by T% or R% monitoring on the coated substrates
- Software interface for real time deposition monitoring
Deposited materials
Metals, Oxides, Nitrides, Carbides, Semiconductors, Carbon Based Materials
Similar technologies
Magnetron Sputtering
a robust solution enabling the widest range of deposited materials