Etching Process
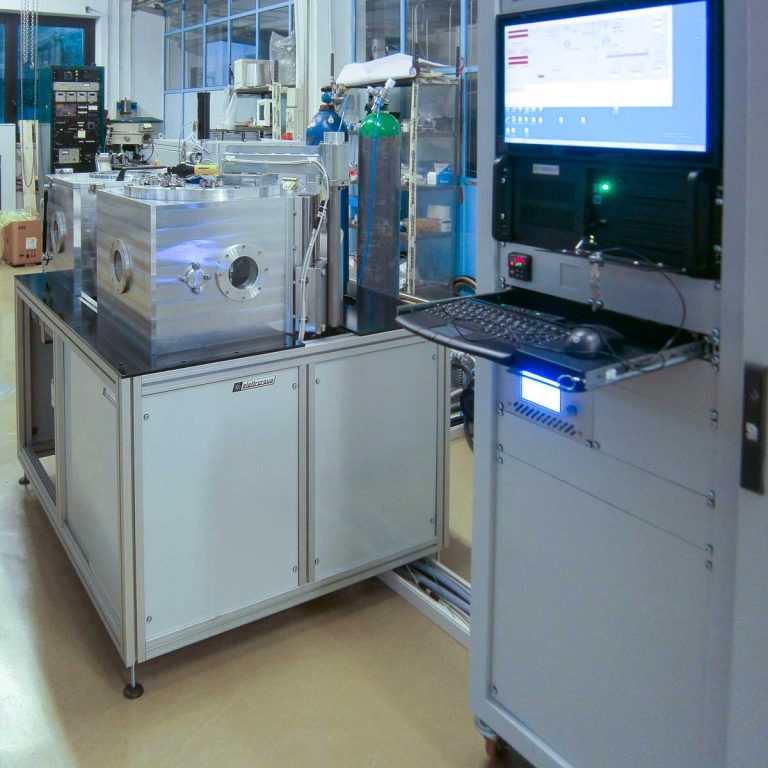
Reactive Ion Etching
RIE
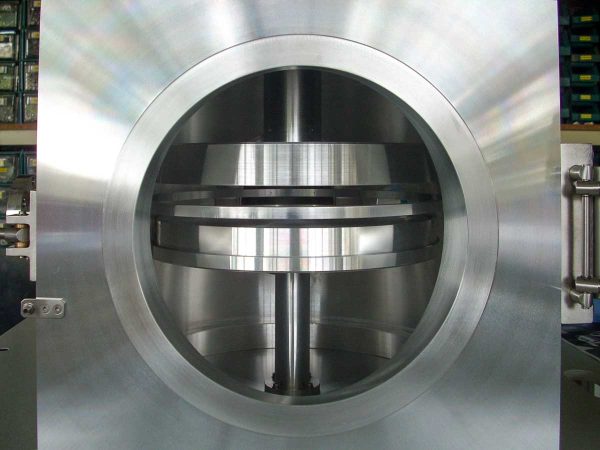
Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) is a plasma-based etching method used to remove material from a substrate surface. During RIE, gas species are activated within the plasma discharge area and transported to the substrate surface through diffusion. A negative electric bias then accelerates these species to the substrate surface to perform etching. When the substrate surface is exposed to the reactant, three processes take place: absorption of the precursors onto the surface, reaction with the substrates surface, and then desorption as volatile reaction products. These reaction products diffuse back to the plasma and are exhausted by a vacuum pump. Typically, a mask is used to pattern the substrates surface, allowing for selective etching in certain areas.

Applications
RIE applications range from low and high-power semiconductors for trenches and vias realization, MEMS for elimination of sacrificial material and general feature definition, de-processing and failure analysis, which makes RIE a key technique to be available in most semiconductor R&D and production facilities.
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive Industry
- Solar energy
- Aerospace and Defence
- Healthcare and medical devices
- Optics and Photonics
- Wear resistant coatings
Key features
- Substrate cooling down to -35 °C
- Single or multiple automatic or manual load lock and manipulators
- Optional optical emission spectrometer for insitu plasma diagnostics and End Point Detection
- Optional real-time, in-situ, plasma etch depth monitoring and end point detection plus colinear wafer vision system
- Different plasma sources can be selected from DC, DC pulsed, RF
- Different reactive gases (02 , H2, N2, C2H4 , CF4, SF6, etc.) can be used during etching process
Etched materials
Metals, Oxides, Nitrides, Carbides, Semiconductors, Carbon Based Materials, Organics
Similar technologies
Reactive Ion Etching
the most common and affordable choice for high quality anisotropic etching