CVD Process
Inductively Coupled Plasma CVD
ICPCVD
Inductively Coupled Plasma Chemical Vapour Deposition is a plasma-based deposition method used to deposit material on a substrate surface. This plasma is generated by an RF generator in an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) source, resulting in higher plasma densities compared to the capacitive coupled plasma (CCP) used in standard PECVD techniques.
The process gases are decomposed into ions and radicals, which are then deposited as thin films on the substrate surface. Due to the higher plasma density, the deposition process can be carried out at lower temperatures (as low as 100 °C), making it suitable for deposition on temperature-sensitive substrates such as polymers.

Applications
ICPCVD is a common method for depositing High-quality semiconductors and dielectrics for applications like low and high-power semiconductor devices, photovoltaic solar cells’ active layers, metalinsulator-metal (MIM) capacitors, laser diodes, sensors, detectors, LEDs, thin film transistors, and so on
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive Industry
- Aerospace and Defence
- Healthcare and medical devices
- Optics and Photonics
- Energy storage
- Wear resisant coating
Key features
- High power ICP RF source
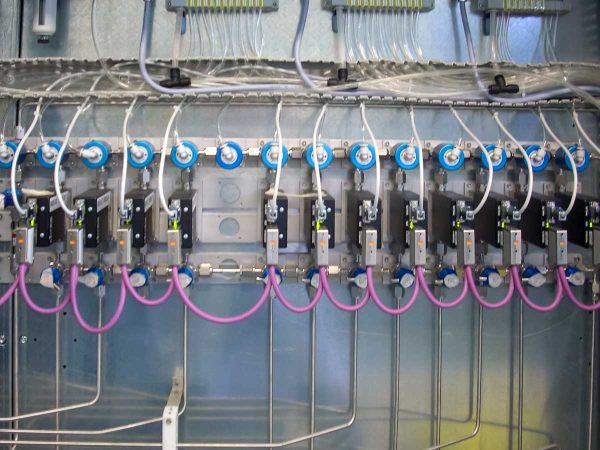
- Modular process gas manifold with mass flow controllers for up to 12 gases
- Optional vapor source controller for liquid Precursor (i.e. TEOS) with tank/cylinder in a closed cabinet for automatic and safe refill
- Automatic process pressure control by throttle valve and capacitance manometer
- In situ spectroscopic plasma monitoring
- Optional automatic or manual load lock (optional pre-heating and/ or plasma treatments)
- Optional wide range optical thickness monitor for the control of layer thickness
- Optional in situ spectroscopic ellipsometry for thickness measurement
Deposited materials
Metals, Oxides, Nitrides, Carbides, Semiconductors, Carbon Based Materials, Organics
Similar technologies
Inductively Coupled Plasma CVD
the right choice for obtaining high density compound materials mixing gaseous and/or liquid precursors at any temperature



