CVD Process
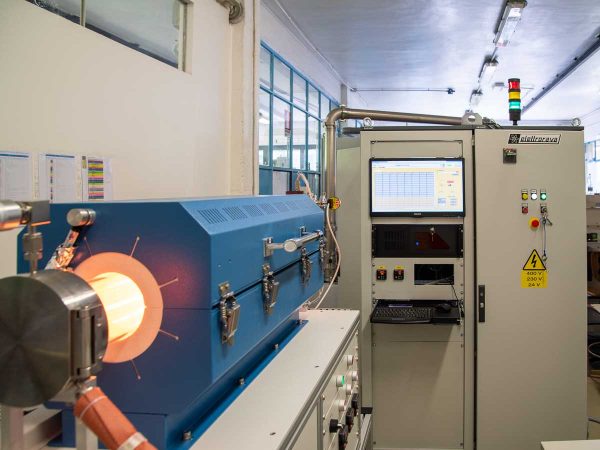
Thermal Low Pressure CVD
LPCVD
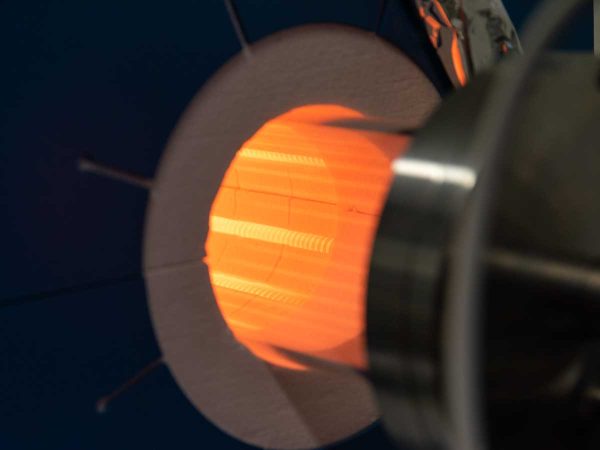
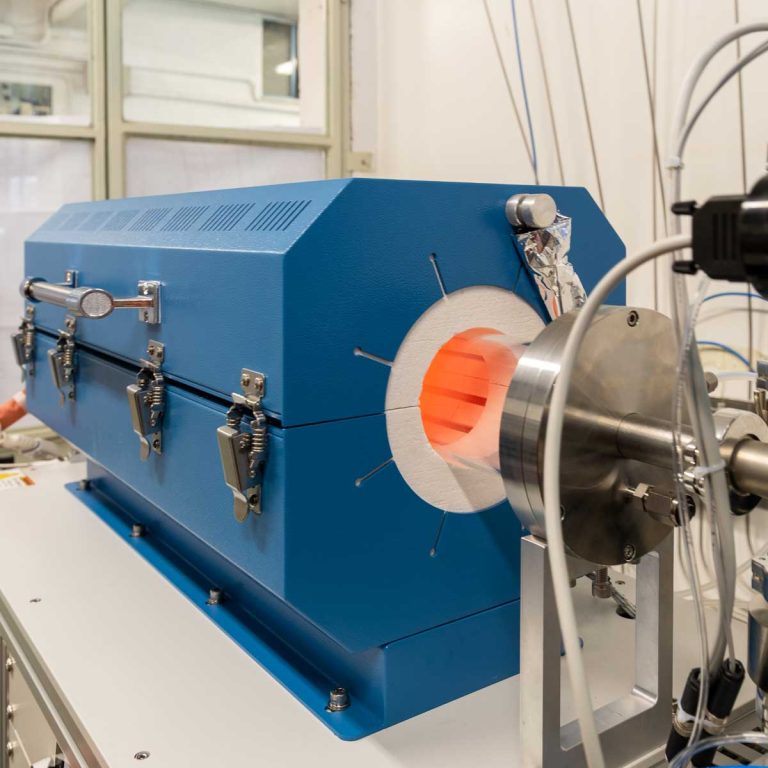
Thermal Low Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (TLPCVD) is a method of depositing thin films on a substrate surface through a thermally activated chemical reaction between one or more reactive gases and the substrate. This deposition technique is used for the deposition of silicon, silicon dioxide, silicon nitride and for the production of carbon nanotubes and graphene. In thermal CVD process, the precursor gas molecules are introduced into a heated chamber in vacuum atmosphere, reacting with the substrate surface at high temperatures, depositing a thin film of the desired material onto the substrate. The substrate is heated to provide the energy needed for precursor reaction and/or decomposition, because the high temperature enables the gas to react with the substrate, improving crystallinity and density of the thin film
Applications
Thermal CVD is a common method for depositing various materials including Silicon Oxide (SiO2), Silicon Nitride (Si3N4), Silicon Carbide (SiC), transition metal oxides (Ta2O5 , TiO2 , and ZrO2 ), transition metal silicates (SiO2)–(ZrO2) alloys, and carbon-based materials like graphene and carbon nanotubes.
- Consumer Electronics
- Aerospace and defence
- Healthcare and medical devices
- Optics and photonics
- Energy storage
- Catalysis
Key features
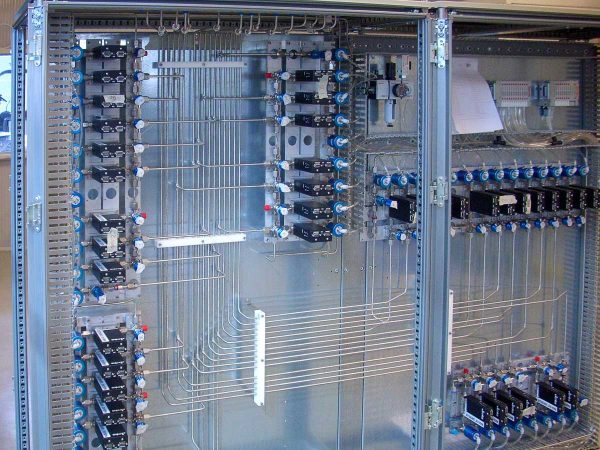
- Hot Wall CVD or LPCVD configuration, up to 1200 °C. Precise and auto tuneable temperature control with completely settable ramp parameters
- Single or multiple furnaces in Hot Wall or Quartz Tube configuration
- Reactive gases (SiH4 , NH3 , H2 , CH4 , N2 , etc.) and/ or liquid precursors controlled directly from the software
- Optional vapor source controller for liquid Precursor with tank/cylinder in a closed cabinet for safe refill
- Optional single or multiple automatic or manual load lock with optional pre-heating and/or plasma treatments
Deposited materials
Oxides, Nitrides, Carbides, Semiconductors, Carbon Based Materials, Organics
Similar technologies
Thermal Low Pressure CVD
a reliable and affordable technology for a wide range of deposited materials