pvd PROCESS
Thermal Evaporation
TE
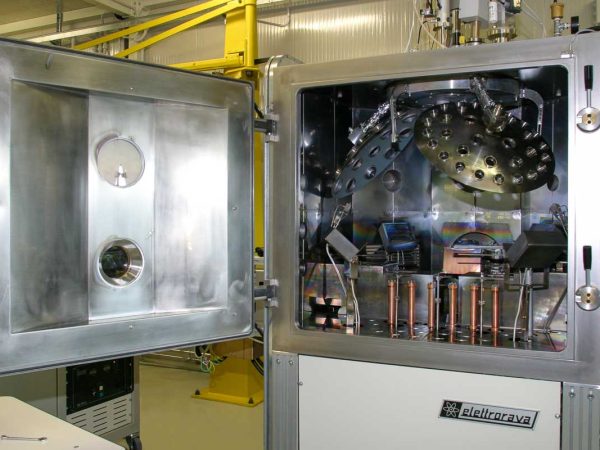
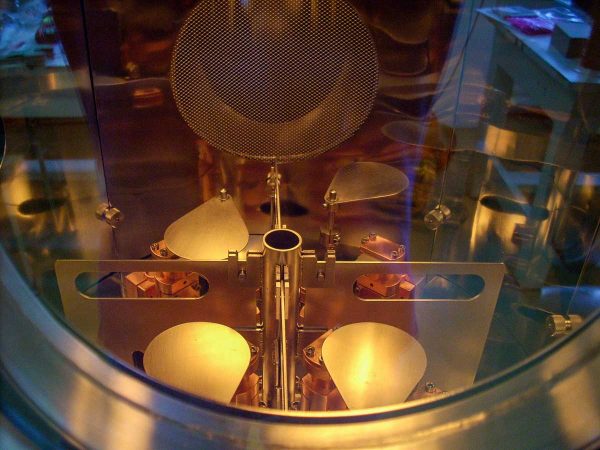
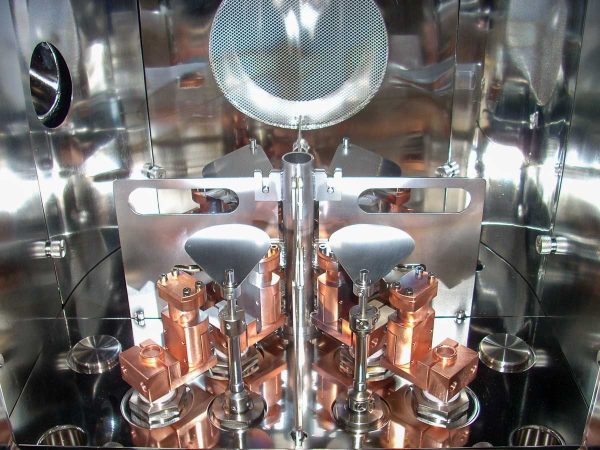
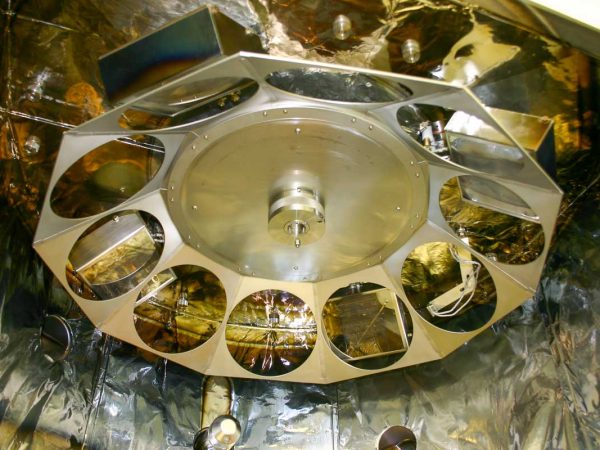
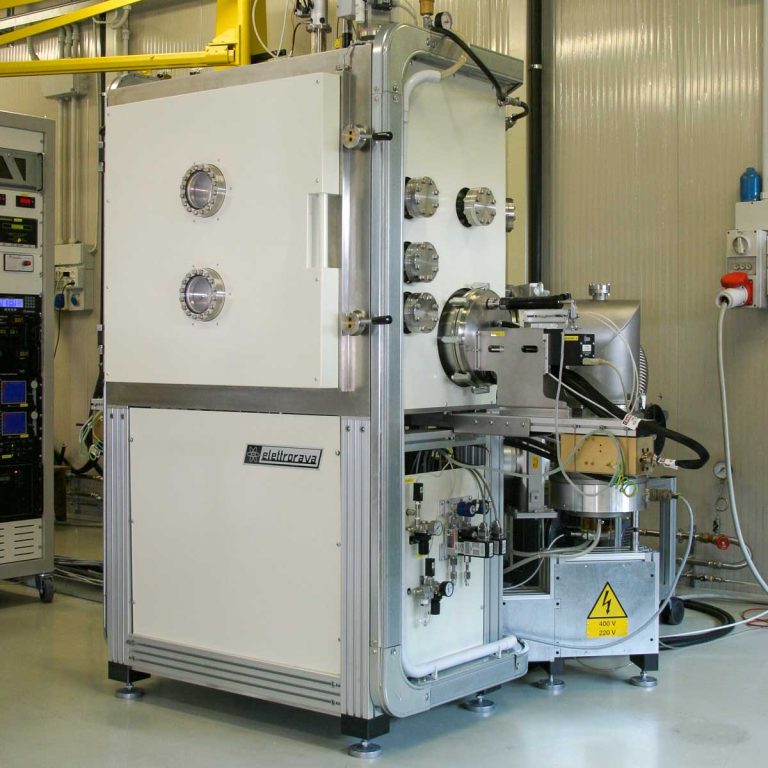
Thermal Evaporation (TE) is a physical deposition technique used to create thin films on a substrate surface by evaporating a solid material. This versatile method allows for the deposition of a wide range of materials, like aluminium, gold, silver, nickel, chrome, etc. The material is located in a crucible, in a chamber kept in a high vacuum environment, and is subject to heating, until the temperature reaches the material evaporation point, when it starts to evaporate. The resulting vaporized molecules travel to the substrate surface, where they nucleate and form the thin film. It is possible to deposit organic materials too using this technique, but it requires precise temperature control, often achieved through the use of a source similar to an effusion cell.

Applications
Thermal evaporation is a popular technique for producing electric contacts and metal layers in
the semiconductor industry, as well as for R&D purposes in microelectronics. Moreover, organic
thermal evaporation can be used for manufacturing optical antireflective coatings for glasses and lenses, as well as for organic electronics, OLEDs, and other applications.
- Microelectronics
- Automotive Industry
- Aerospace and Defence
- Healthcare and medical devices
- Optics and Photonics
- Energy storage
- Wearable technology
Key features
- HV or UHV configuration
- Single or multiple coils, boats, crucibles, or Knudsen effusion Cells
- Reactive gases (02 , N2 , etc) can be added for direct reaction during deposition process
- Fully integrated quartz crystal controller for the automatic control of the thickness as well as for programming multilayers and deposition rate in each layer, directly from main software
- Optional automatic or manual load lock with optional pre-heating and / or plasma treatments
- Optional wide range optical thickness monitor for the control of layer thickness.
Deposited materials
Metals, Oxides, Semiconductors, Organics
Similar technologies
Thermal Evaporation
a reliable and affordable technology for a wide range of deposited materials





